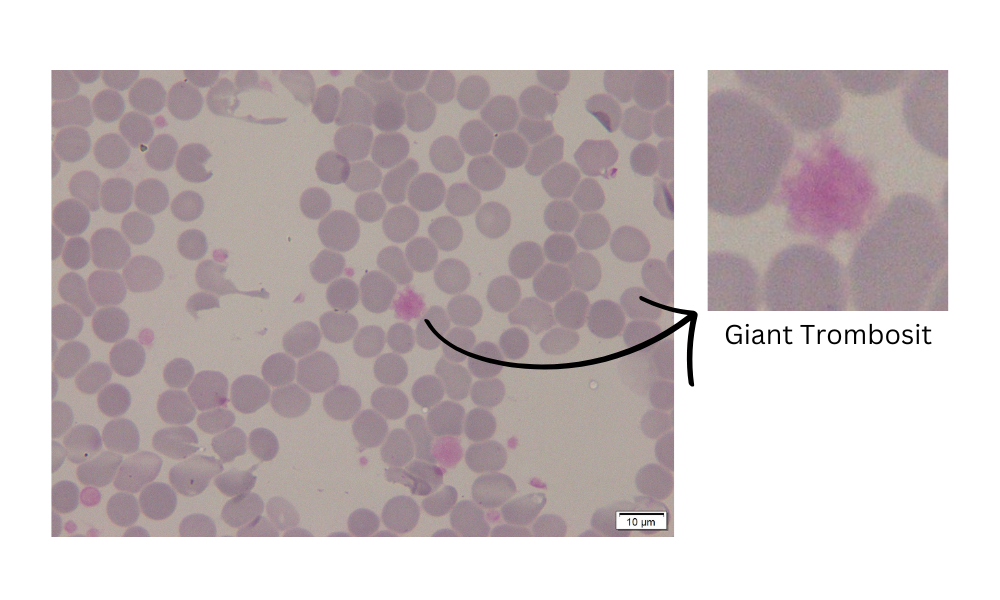
Giant Trombosit Class
The detection system classifies the largest probability of detection results belonging to the Giant Platelet Class.
Gambar mikroskopis dengan giant trombosit (Fitri dkk., 2017).
The presence of giant platelets in blood test results is one indication of Essential Thrombocythemia disease. Essential Thrombocythemia (ET) is myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) affected by thrombocytosis, which is an excessive increase in platelet count (Tefferi & Barbui, 2020). The condition of patients with bone marrow that produces too many platelets and an increase in anisocytosis is generally found giant platelets or giant platelets (Nanda Imron & Fitri, 2019). An increase in excess platelet count accompanied by the presence of giant platelets is an indication of Essential Thrombocythemia (ET) disease. Giant platelets have a diameter as large as leukocytes or erythrocytes.
Some of the methods used to diagnose ET are full blood count (FBC) and microscopic examination. In the FBC examination, some of the criteria found in ET patients are as follows:
- There is an increase in platelet count where platelets are found in a large variety of sizes and shapes.
- Sometimes there is also an increase in leukocyte counts where basophil leukocytosis is common in all chronic myeloproliferative diseases.
- Hemoglobin, hematocrit and erythrocyte counts vary and anemia is commonly microcytic due to iron deficiency or macrocytic due to increased folate (Fitri et al., 2017).